In the first two quarters of FY2013, Apple realized a revenue growth rate of 14.73% to $98.115 billion dollars. In the first two quarters of FY2012, which included an additional shipping week, Apple's revenue rose 66% year-over-year, setting a very challenging growth comparison for the six-month period ended in March.
There's no disputing the fact Apple's revenue growth rate has slowed and the company is presently locked in a cycle of lowered rates of revenue growth through at least the June quarter. The consensus revenue estimate for this fiscal year currently stands at $171.44 billion or 9.50% revenue growth. Even more sobering is the conservative revenue growth estimate for FY2014. At this time, the consensus for FY2014 suggests revenue of $188.12 billion and a growth rate of only 9.70%. The consensus revenue growth estimate of 9.50% for this fiscal year is in stark contrast to the 44.58% revenue growth achieved in the fiscal year ended last September.
Apple manages its business on a geographic basis. In today's article I will look at Apple's revenue by region for the first six months of this fiscal year. Apple's revenue performance by region provides insight into the reasons for the slow rate of revenue growth and clues to the manner in which Apple can reignite growth over the next several fiscal quarters.
Apple's Revenue By Region
The chart below illustrates the percentage of recognized revenue contributed by each of Apple's six regional revenue segments in the first six months of the current fiscal year.
In the first six months of the current fiscal year, roughly 58% of Apple's recognized revenue was sourced in the Americas and Europe, exclusive of the retail stores. With the high concentration of Apple retail stores in the Americas and Europe, Apple's revenue growth remains highly dependent on performance in the two geographic regions.
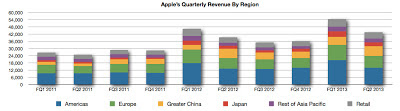
The graph below illustrates Apple's revenue by region over the most recent ten fiscal quarters.
The graph below illustrates Apple's revenue by region over the most recent ten fiscal quarters.
Although the rate of revenue growth has slowed and earnings per share growth turned negative in the first six months of the current fiscal year, Apple will continue to generate revenue growth on a quarterly basis for the foreseeable future. Management's June quarter revenue guidance of between $33.5 billion and $35.5 billion suggests Apple's revenue growth rate will reach its nadir in the current quarter. Last year, June quarter revenue was $35 billion.
In the first half of FY2013 iPad unit sales rose 55.5% while revenue from iPad sales rose 29.2%. This is due primarily to the introduction of the iPad mini and the drop in average selling price per unit to $459 from $552 in the prior-year period. In the first half of FY2013, iPhone revenue rose 16% on an 18% increase in unit sales. The average iPhone selling price dropped slightly from $641 to $629 in the first half of the current fiscal year.
There are strongly held views Apple needs to introduce a lower cost iPhone to boost unit sales growth particularly in emerging markets. However, the rate of revenue growth would considerably trail the rate of unit sales growth if Apple chooses this path for its top-selling device line. Returning to faster rates of revenue growth requires more than releasing lower cost versions of current devices. There are opportunities for revenue growth in emerging markets. But returning to higher rates of overall growth will require much stronger revenue growth performances in the Americas (primarily the United States) and Europe.
Quarterly Percentages of Revenue By Region
The graph below illustrates Apple's percentage of revenue by region over the same ten fiscal quarters.
Apple has a highly seasonal revenue pattern based in part of the refresh cycles of the iPhone and iPad lines. Despite slower rates of growth in the Americas and Europe, the two regions combined continue to deliver the majority of the company's revenue. Even with comparatively faster rates of revenue growth in Greater China, Japan and the Rest of Asia Pacific, the Americas and Europe will have the greatest impact on the company's overall rate of revenue growth.
Revenue Growth By Region
The graph below illustrates Apple's rates of revenue growth by region for the first six months of the current fiscal year.
Over this six-month period, Apple's revenue growth rates in the Americas, Europe and Apple Retail hovered around 11% year-over-year. During this period Greater China delivered 28% revenue growth, Japan delivered 22% revenue growth and the Rest of Asia Pacific delivered 17% revenue growth. Combined, the Americas, Europe and Apple Retail segments represented about 70% of reported revenue. The concentration of revenue in the Americas and Europe along with the concentration of retail stores in the two geographic areas highly influenced the overall revenue growth rate of 14.73%.
Returning to faster rates of revenue growth will require new products and services in Apple's largest revenue regions whether or not Apple chooses to release lower cost iPhone handsets in emerging markets.
Revenue Segment Operating Income Per Revenue Dollar
The graph below illustrates Apple's revenue segment operating income per revenue dollar.
Over the most recent ten fiscal quarters, Japan and Greater China, on average, have delivered the highest operating income per revenue dollar among Apple's six regional revenue segments. Currently, the iPhone is not available on the largest cellular services provider in either region.
Due in large part to the economies of scale achieved from two iPhone 4 series handsets in the market, Apple attained extraordinarily high gross margin in the first half of FY 2012. There will be a similar occurrence in the first half of FY2014 with two iPhone 5 series handsets in the global market. Apple's gross margin averaged 45.9% in the first half of FY2012 versus 38.1% in the first half of FY2013. While I don't expect gross margin to reach early FY2012 levels in the first six months of FY2014, Apple can achieve both revenue growth and net income growth in the first half of FY2014 with iPhone 5 series economies of scale, the addition of Greater China's China Mobile as an authorized iPhone carrier and the addition of Japan's NTT DoCoMo.
A lower cost iPhone handset for markets outside the US and Europe might spur revenue growth, but revenue and earnings growth moving forward require more than lower cost products. It will require new products and services for the global market. The release of the iPad mini has demonstrated lower cost versions of products can increase unit sales. But lower cost products will pressure gross margin and net income per revenue dollar.
In Greater China, Japan and the Rest of Asia Pacific, Apple is currently achieving revenue growth rates greater than the rate of revenue growth for the company as a whole. Japan is also delivering consistently high operating income per revenue dollar.
WWDC 2013 and Apple TV
On June 10th Apple will convene its annual conference for developers. Conference registration for this year's event sold out literally in seconds. I've mentioned in previous articles the importance of Apple's iTunes/Software/Services segment and the quickening pace of payments to developers.
In the first half of FY2013, the revenue segment delivered 26% revenue growth to $7.8 billion and represented about 8% of Apple's reported revenue total. It isn't enough to sell more devices. As an eco-system Apple must expand the market for developers in all regions and expand the market for developers through all device lines.
At this year's conference I expect Apple to announce an SDK for Apple TV. While there's been much talk of Apple bringing to market an HD TV, opening the existing Apple TV digital media receiver for developers would be an important step forward in Apple's efforts to provide new markets for developers and expand the company's presence in the living room.
I also expect Apple to announce the company will incorporate 802.11ac in its next generation of products. High throughput wireless technology is essential for what I expect to be Apple's product and services assault on the living room entertainment experience and it's important to the delivery and sharing of rich content across device lines.
Apple's Revenue Growth Moving Forward
There isn't a single solution for Apple's management in its efforts to reignite revenue and earnings growth. Solutions include an expansion of current iPhone carriers, perhaps the release of a less expensive iPhone for emerging markets and new products and services for Apple's existing product markets in the United States and throughout Europe.
The global smartphone market is fast approaching a mature market phase. As an eco-system, Apple needs to determine what new products can be brought to market not only in emerging economies but also in its established markets that will continue to generate much of the company's revenue and greatly influence the company's overall revenue growth performance.
Apple's future growth depends at least as much on the product platform the company continues to develop as it depends on the product lines the company has already brought to market.
Apple's future growth depends at least as much on the product platform the company continues to develop as it depends on the product lines the company has already brought to market.
Robert Paul Leitao
Disclosure: The author is long Apple shares